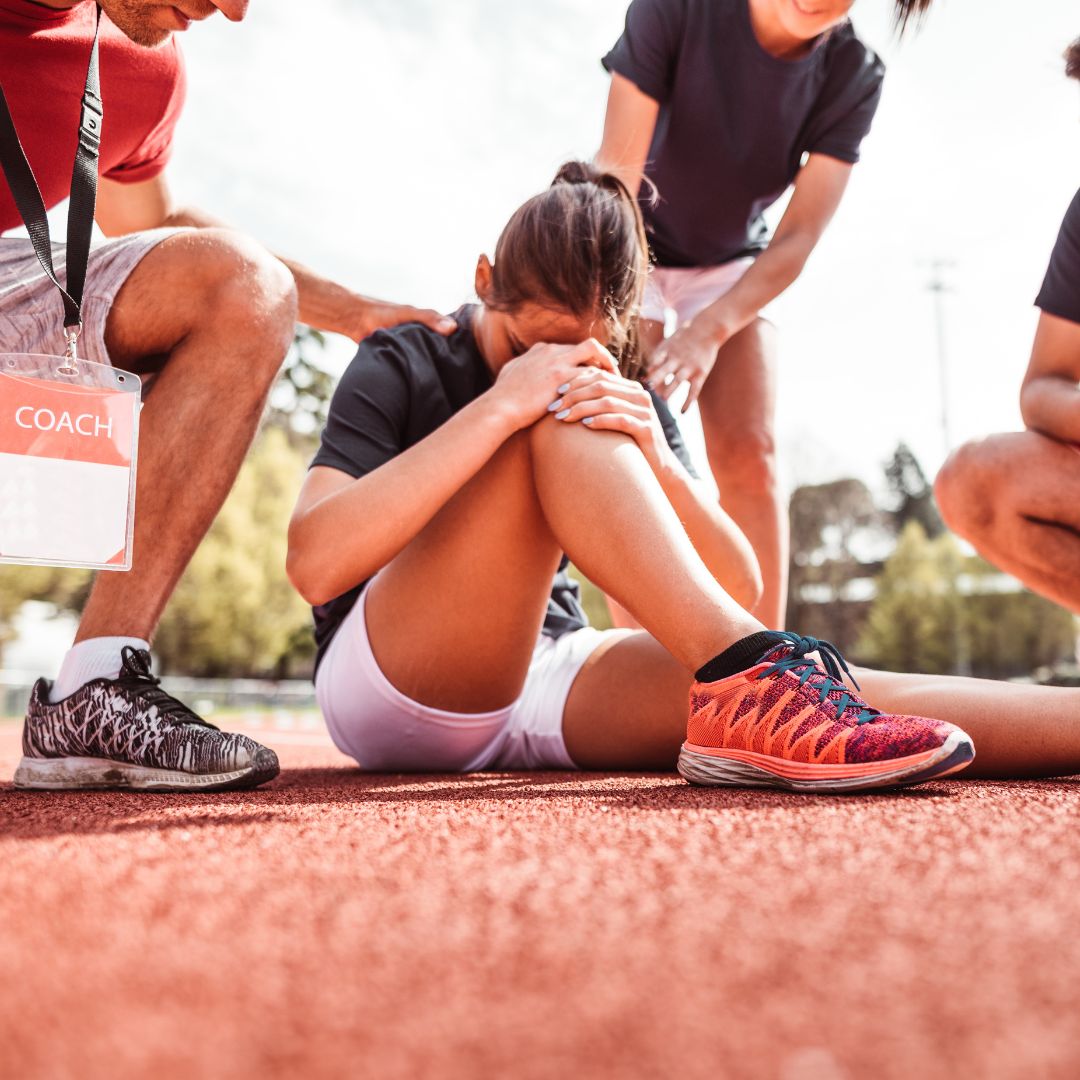
Sports Psychologist in Baltimore, MD
You want to work on your mental game, but how do you train your brain?
At MindBalanceSPORT, We Train The Other Half Of The Athlete.
You want to work on your mental game, but how do you train your brain?
Mental training does not get much media attention, but at MindBalanceSPORT we know it is a game changer. The mental skills you will learn at MindBalanceSPORT are generalizable in the classroom, in sport and in life!
We know that mental skills can be successfully taught, even at an early age.

Our Services
Meet the Team





testimonials
Athlete Stories: Real Comebacks, Real Results

Emma, a high school basketball player, tore her ACL in the middle of her junior season. After surgery, she struggled with self-doubt and fear every time she stepped back on the court. Through sport psychology training, she learned visualization techniques and confidence-building exercises that helped her regain trust in her knee. When she returned for her senior season, she didn’t just play—she led her team to the playoffs.

Carlos, a soccer player, suffered a stress fracture in his foot and had to miss half of his season. Sitting out was mentally tougher than the pain itself. We worked on mental engagement strategies to keep him sharp—studying game film, setting small rehab goals, and using mental imagery to stay ready. When he was finally cleared, his confidence never wavered.

Jordan, a track athlete, strained her hamstring before a major competition. She feared losing speed and falling behind competitors. Instead of focusing on what she couldn’t do, we redirected her energy toward mental preparation, using self-talk and goal setting to keep her confidence strong. When she returned, she set a new personal record.
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. It was a great help to my 14-year-old competitive volleyball player daughter. Raven was great to understand and connect with her from start to end. We will continue with our sessions as needed.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Great results! I’ve loved working with Paula. Our sessions have greatly improved both the physical and mental aspects of my tennis game. I’m playing better and having more fun! Highly recommend!Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Our family had a wonderful experience with Paula Castro. We needed some additional confidence in a particular area/sport and Paula helped get us there. We know who to turn to if we need help again. She’s been a Blessing. Thank you, Paula!Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I highly recommend MindBalanceSPORT. Our son works with John Howard. John is very caring, positive, and effective at working with teenagers. John is an adept listener and created an individualized plan tailored to our son’s personality. After just a few sessions with John, we noticed a significant improvement in our son’s motivation and mental approach to sports and life in general. Our son looks forward to meeting with John and tells us that he benefits immensely from their connection.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Paula Castro is an outstanding professional on the field. She has helped my daughter improve her confidence, preparation, and thanks to these session she feels more prepared and motivated. Paula takes the time also to share (what she can) and align with us as parents to be on the same page. Strongly recommended!Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. MineBalanceSPORT has quickly become the area's expert in sports psychology. Their reputation is well deserved given their incredibly thoughtful, scientifically based approaches to treating performance-related conditions, and I have only heard glowing, positive feedback from those who have engaged in their program. I will also add that Drs. Jones and Chirby presented to us (our group comprises of 15+ doctors and masters level clinicans) about their program and impressed us all with their level of expertise and passion for this field. I give them my highest recommendation.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr. Jones was beyond helpful to me throughout our time together. If you are an athlete and you need advice or assistance this is the place to come to. She completely changed my outlook and mindset in a time when I needed her most. I look forward to staying in touch with her and am forever thankful for her expertise.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Paula has been a huge help with my daughter Morgan coming off her injury. It’s been 18 months since she’s played basketball and she’s thriving because I know Paula is guiding her the right direction. As a mother, I’m extremely gratefulTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. If you are looking for Amazing Psychologists who can help support you in your sports performance, you need to call MindBalanceSPORT! Dr. Chirby and her colleagues are a wealth of knowledge, they have so many helpful techniques for mind balance, and they have so much compassion for the communities that they serve! Highly recommend!!!
Recovery
While Everyone Has A Physical Ceiling, There Is No Mental Ceiling.
Effective Goal Setting Techniques with Sports Psychologists in Baltimore, MD to Boost Athletic Performance
Effective Goal Setting Techniques with Sports Psychologists in Baltimore, MD to Boost Athletic Performance
Goal setting is a fundamental practice in sports psychology that helps athletes improve focus, motivation, and overall performance. By providing structure and direction, effective goal setting enables athletes to measure progress and stay committed to their aspirations. Below are techniques and best practices for goal setting and monitoring that can significantly enhance athletic performance.
Types of Goals in Sports Psychology
- Outcome Goals: Focus on the results of competitions (e.g., winning a championship or achieving a specific ranking).
- Performance Goals: Emphasize personal standards, such as running a mile in under six minutes or improving accuracy in free throws.
- Process Goals: Concentrate on the specific actions or techniques required during training or competition (e.g., maintaining proper posture during weightlifting).
SMART Goals Framework
| Criteria | Description | Example for Athletes |
| Specific | Clearly define what you want to achieve | “Increase my batting average by 10%.” |
| Measurable | Include metrics to track progress | “Track weekly improvement through game stats.” |
| Achievable | Ensure the goal is realistic within your ability | “Run 5 km three times per week consistently.” |
| Relevant | Align with broader objectives | “Enhance endurance for an upcoming marathon.” |
| Time-bound | Set a deadline for achieving the goal | “Achieve this improvement within 3 months.” |
Techniques for Effective Goal Setting
- Dividing long-term aspirations into manageable short-term targets can prevent feelings of overwhelm.
- Example: For an athlete training for an Ironman triathlon, weekly improvements in swimming distance or cycling speed can serve as stepping stones.
- Individual athletes should focus on personal development goals while working collaboratively with teammates to achieve group success.
- Schedule periodic check-ins to evaluate progress.
- Adjust objectives based on new challenges, injuries, or changes in priorities.
- External input can provide valuable insights into areas needing improvement.
- Constructive criticism helps refine both process goals and performance strategies.
Monitoring Progress
- Performance Logs: Daily journals where athletes record training details, diet habits, mental states, and outcomes.
- Wearable Technology: Devices like fitness trackers help monitor metrics such as heart rate, distance covered, or calories burned.
- Video Analysis Tools: Reviewing footage of performances highlights strengths and identifies areas requiring refinement.
By combining structured goal-setting methods with consistent monitoring practices, athletes can optimize their mental preparation while staying motivated throughout their journey. Properly implemented strategies not only improve physical outcomes but also foster resilience and confidence necessary for excelling in competitive environments.
How Sports Counselling in Baltimore, MD Helps Athletes Achieve Their Goals
Effective goal setting is a cornerstone of sports psychology, helping athletes develop a clear roadmap for achieving success. Sports psychologists utilize specific techniques to ensure that goals are not only motivating but also measurable and achievable. This structured approach plays a critical role in enhancing both performance and mental strength.
The Importance of Goal Setting in Athletics
- Providing Direction: Clear goals give athletes a sense of purpose and focus during training and competition.
- Enhancing Motivation: Well-defined objectives inspire consistent effort and perseverance.
- Building Confidence: Achieving smaller, incremental goals fosters self-belief and prepares athletes for larger challenges.
- Improving Performance: Goals help identify areas that need improvement while encouraging accountability.
By aligning physical training with psychological preparation, sports psychologists ensure that goals are meaningful and tailored to the athlete’s abilities.
How a Sports Mental Coach in Baltimore, MD Helps Athletes Set Effective Goals
| Type | Description | Example |
| Outcome Goals | Focused on the end result or competitive achievements | Winning a tournament or securing a medal |
| Performance Goals | Related to improving specific performance metrics | Increasing sprint speed by 5% |
| Process Goals | Centered on mastering techniques or behaviors | Keeping proper form during weightlifting |
Each type of goal serves a unique purpose, and athletes benefit most when these categories are interlinked.
SMART Goal Framework
- Specific: Clearly define the objective (e.g., “Improve free throw accuracy to 85%”).
- Measurable: Ensure progress can be tracked with tangible metrics.
- Achievable: Set realistic yet challenging goals based on current capabilities.
- Relevant: Align the goal with overall athletic ambitions.
- Time-bound: Establish deadlines to maintain urgency and focus.
For example, instead of saying “I want to get better at running,” an athlete might set a SMART goal like “Run 5 kilometers in under 25 minutes within three months.”
Strategies for Effective Goal Monitoring
- Athletes are encouraged to maintain training logs or journals where they document daily progress, challenges faced, and accomplishments achieved.
- Recording practices or competitions can help identify areas requiring improvement while reinforcing successful actions.
- Regular meetings between athletes and their coaches or psychologists provide an opportunity to recalibrate goals if necessary.
- Wearable devices or apps can track metrics like heart rate, distance covered, or calories burned in real-time.
These methods not only keep athletes accountable but also allow them to celebrate incremental successes along their journey.
Common Pitfalls in Goal Setting
- Setting overly ambitious targets without considering feasibility.
- Focusing too much on outcome goals while neglecting process-oriented improvements.
- Failing to adapt or adjust goals when circumstances change (e.g., injuries).
Sports psychologists help mitigate these issues by fostering flexibility in planning while maintaining high standards.
Goal setting facilitates consistent progress toward athletic excellence. By breaking down large ambitions into manageable steps with clear parameters for success, sports psychologists empower athletes to overcome barriers both physically and mentally.
How Performance Psychology in Baltimore, MD Helps Athletes Achieve Success Through Goal Setting
Goal setting is a cornerstone of sports psychology, serving as a powerful tool to help athletes achieve their maximum potential. Sports psychologists use structured techniques to guide athletes in setting, pursuing, and achieving goals that align with their personal and professional aspirations. Below are some of the ways goal setting is employed and monitored to foster success among athletes.
The Importance of Goal Setting in Sport Performance Training in Baltimore, MD
Goal setting provides athletes with focus, direction, and motivation. By breaking down larger objectives into measurable steps, it is easier for individuals to maintain progress while fostering a sense of accomplishment.
Key benefits of goal setting include: – Increased Motivation: Clear goals provide a tangible endpoint for athletes to work toward. – Improved Focus: By specifying objectives, attention remains on the task at hand instead of unnecessary distractions. – Enhanced Confidence: Achieving smaller milestones builds self-belief over time. – Accountability: Defined targets allow both athletes and coaches to track progress objectively.
Types of Goals Used by Sports Psychologists
| Type of Goal | Description | Example |
| Outcome Goals | Focus on the ultimate result or achievement. | Winning a championship or breaking a record. |
| Performance Goals | Emphasize individual performance improvements rather than external results. | Increasing sprint speed by 5% in 3 months. |
| Process Goals | Concentrate on specific actions or techniques needed to improve performance consistently. | Practicing free throws for 30 minutes daily. |
Effective Goal Setting Techniques in Sports Psychiatry in Baltimore, MD
- Specific: Goals must be clear and precise.
- Measurable: Progress should be quantifiable.
- Achievable: Targets need to be realistically attainable within the athlete’s abilities.
- Relevant: Objectives should align with broader career aspirations and values.
- Time-Bound: Deadlines ensure accountability.
- Breaking down long-term aspirations into smaller, manageable short-term goals allows athletes to maintain momentum over time.
- Athletes are encouraged to visualize not only achieving their goals but also overcoming challenges along the way.
- Regular feedback helps assess whether an athlete’s current strategies are effective or require adjustment.
Overcoming Goal-Setting Challenges with a Sports Psychologist Near Me
- Overambitious Targets
Unrealistic goals can lead to frustration or burnout if progress seems unattainable. To fix this, psychologists emphasize realistic goal-setting through achievable benchmarks. - Lack of Motivation Over Time
Sustaining enthusiasm can be difficult during long training cycles. Providing regular rewards tied to smaller milestones can help keep engagement high. - Fear of Failure
Fear often prevents athletes from pursuing ambitious objectives altogether. Psychologists address this through cognitive restructuring techniques that promote resilience and optimism.
Goal setting in sports psychology goes beyond simply writing down aspirations—it involves strategic planning, mental preparation, and consistent evaluation that enables athletes not only to perform better but also grow mentally stronger throughout their journey toward success.
How Sports Psychologists Use Goal Setting to Foster Success in Athletes
Goal setting is a fundamental technique used by sports psychologists to help athletes enhance their performance, maintain focus, and build confidence. It serves as a structured approach to achieving both short-term and long-term objectives while keeping athletes motivated throughout their journey. Below is an in-depth explanation of how goal setting is employed by sports psychologists and why it is so effective.
Types of Goals in Sports Psychology
- Outcome Goals
Focus on the desired result or achievement, such as winning a championship or breaking a record. These goals depend not only on the athlete’s performance but also on external factors like competitors. - Performance Goals
Centered around personal benchmarks that are within the athlete’s control, such as improving speed, strength, or accuracy. For example: - Reducing a 100-meter sprint time by 0.2 seconds.
- Increasing free throw accuracy from 75% to 85%.
- Process Goals
Emphasize the actions or behaviors needed to achieve performance improvements, such as practicing footwork drills daily or maintaining proper form during weightlifting.
Principles of Effective Goal Setting
- The SMART Framework:
Goals are tailored using this widely adopted framework: - Specific: Clear and well-defined objectives (e.g., “Run five kilometers in under 20 minutes”).
- Measurable: Progress can be tracked with data (e.g., “Bench press an additional 10 pounds within four weeks”).
- Achievable: Challenging but realistic based on the athlete’s current abilities.
- Relevant: Aligned with overall aspirations and priorities (e.g., improving endurance for triathlon training).
- Time-bound: Includes a deadline for accountability.
- Short-Term vs Long-Term Planning:
Breaking down larger objectives into smaller milestones helps sustain motivation while providing consistent opportunities for reflection and adjustment. - Customization:
Every athlete has unique strengths, weaknesses, and circumstances. Sports psychologists ensure that goals align with individual needs rather than applying generic templates.
Monitoring Progress
- Performance Journals: Athletes document daily practice sessions, including successes, setbacks, and insights gained from each session.
- Checklists: A comprehensive list of activities related to process goals ensures focus remains sharp.
- Feedback Sessions: Regular discussions between the psychologist and athlete allow for fine-tuning strategies based on results.
| Goal Type | Example | Psychological Benefit |
| Outcome Goal | Winning a local marathon | Increases motivation through competition |
| Performance Goal | Improving swim lap time | Builds self-efficacy through measurable gains |
| Process Goal | Practicing visualization techniques daily | Strengthens focus during high-stress moments |
Benefits of Goal Setting in Athletic Performance
When implemented effectively by sports psychologists, goal setting offers several benefits: – Boosts confidence by demonstrating measurable progress. – Enhances focus by clarifying priorities. – Encourages persistence during setbacks by highlighting long-term vision. – Promotes accountability through structured monitoring methods.
By integrating these techniques into training regimens, sports psychologists empower athletes to unlock their full potential while fostering resilience both inside and outside competition settings.
The Role of Self-Care in Achieving Peak Athletic Performance
Self-care is a vital component of peak athletic performance, yet it is often overlooked in high-pressure sports environments. Athletes who prioritize self-care can improve their physical and mental well-being, which directly impacts their ability to perform at their highest level. Below, we explore why self-care matters, its benefits for athletes, and practical strategies to incorporate self-care into daily routines.
Why Self-Care Matters for Athletes
- Injury Prevention: Regular rest and recovery practices help prevent overuse injuries.
- Mental Clarity: Self-care reduces stress and fosters a healthy mindset.
- Sustained Performance: Caring for one’s health ensures long-term success rather than short-lived peaks.
Neglecting self-care can result in diminished performance, increased anxiety, or even fatigue syndromes such as overtraining syndrome (OTS).
Key Benefits of Self-Care in Sports
- Enhanced Recovery
Proper rest allows muscles to repair themselves after intense activity. Practices like sleep optimization and post-workout nutrition are critical components of recovery. - Improved Focus
Mental relaxation techniques such as meditation or journaling can keep an athlete’s mind sharp under pressure. - Better Stress Management
Engaging in activities outside of sports—like spending time with family or hobbies—can reduce emotional strain. - Increased Longevity in Sport
Athletes who practice consistent self-care enjoy longer careers by avoiding chronic injuries or psychological burnout.
Strategies for Integrating Self-Care Into Training
- Include time for rest days to allow both physical and mental rejuvenation.
- Avoid overloading with too many competitions or strenuous training sessions back-to-back.
- Aim for 7–9 hours of sleep each night.
- Develop a bedtime routine that eliminates distractions like screens at least an hour before bed.
- Stretching, yoga, or low-impact exercises like swimming promote blood circulation while easing physical tension.
- Consume balanced meals rich in protein, healthy fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water consistently throughout the day.
- Engage with mindfulness practices such as deep breathing or guided meditation.
- Seek professional support from psychologists when needed.
A Holistic Approach: Physical + Emotional Well-being
| Aspect | Examples of Self-Care Practices | Purpose |
| Physical Recovery | Sleep optimization; hydration; stretching | Reduces fatigue; promotes healing |
| Emotional Wellness | Journaling; talking with friends/family | Reduces anxiety; builds emotional resilience |
| Cognitive Focus | Meditation; reading | Enhances decision-making skills |
Developing habits that address all these areas creates a strong foundation for sustainable athletic success.
By understanding the role of self-care in achieving peak performance—and implementing actionable strategies—athletes can ensure they remain physically prepared and mentally resilient throughout their careers.
Practical Strategies for Incorporating Mindfulness into Sports Psychology
Mindfulness has emerged as a powerful tool in sports psychology, helping athletes improve focus, manage stress, and perform at their best under pressure. Integrating mindfulness practices into athletic training provides both mental and physical benefits that support long-term success. Below are some practical strategies for incorporating mindfulness into sports psychology.
1. Breathing Techniques to Enhance Focus
- Box Breathing: Inhale for four counts, hold for four counts, exhale for four counts, and pause for another four counts before repeating the cycle.
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: Focus on expanding the diaphragm while breathing deeply to stimulate relaxation.
- 4-7-8 Technique: Inhale for four seconds, hold the breath for seven seconds, and exhale slowly over eight seconds.
Regular practice of these methods can aid in reducing anxiety before competitions and enhancing concentration during performance.
2. Visualization to Build Confidence
- Develop muscle memory by vividly imagining executing techniques or plays.
- Build confidence by visualizing success in stressful situations.
- Prepare mentally for unexpected challenges during competition.
For example, a sprinter might visualize crossing the finish line with precise form and speed, reinforcing positive mental imagery.
3. Mindful Movement Practices
| Practice | Benefits |
| Yoga | Improves flexibility, balance, and focus while reducing stress levels. |
| Tai Chi | Encourages fluid motion and builds a connection between breath and movement. |
| Slow Stretching | Enhances body awareness while promoting relaxation after intense workouts. |
These activities not only strengthen the mind-body connection but also help athletes recover effectively.
4. Journaling as a Reflection Tool
- “What went well during today’s training or competition?”
- “What challenges did I face today? How did I respond?”
- “What am I grateful for in my athletic journey?”
This reflective process allows athletes to track emotional patterns, identify areas of growth, and maintain motivation over time.
5. Creating Mindful Routines
- Engaging in short meditation sessions before warm-ups.
- Using affirmations to set positive intentions (e.g., “I am focused,” “I am prepared”).
- Spending five minutes practicing gratitude to foster mental clarity.
These small yet impactful habits create mental stability even under pressure.
By incorporating these strategies into sports psychology frameworks, both amateur and elite athletes can develop resilience, sharpen concentration skills, and achieve peak performance through the power of mindfulness practices tailored to their specific needs.