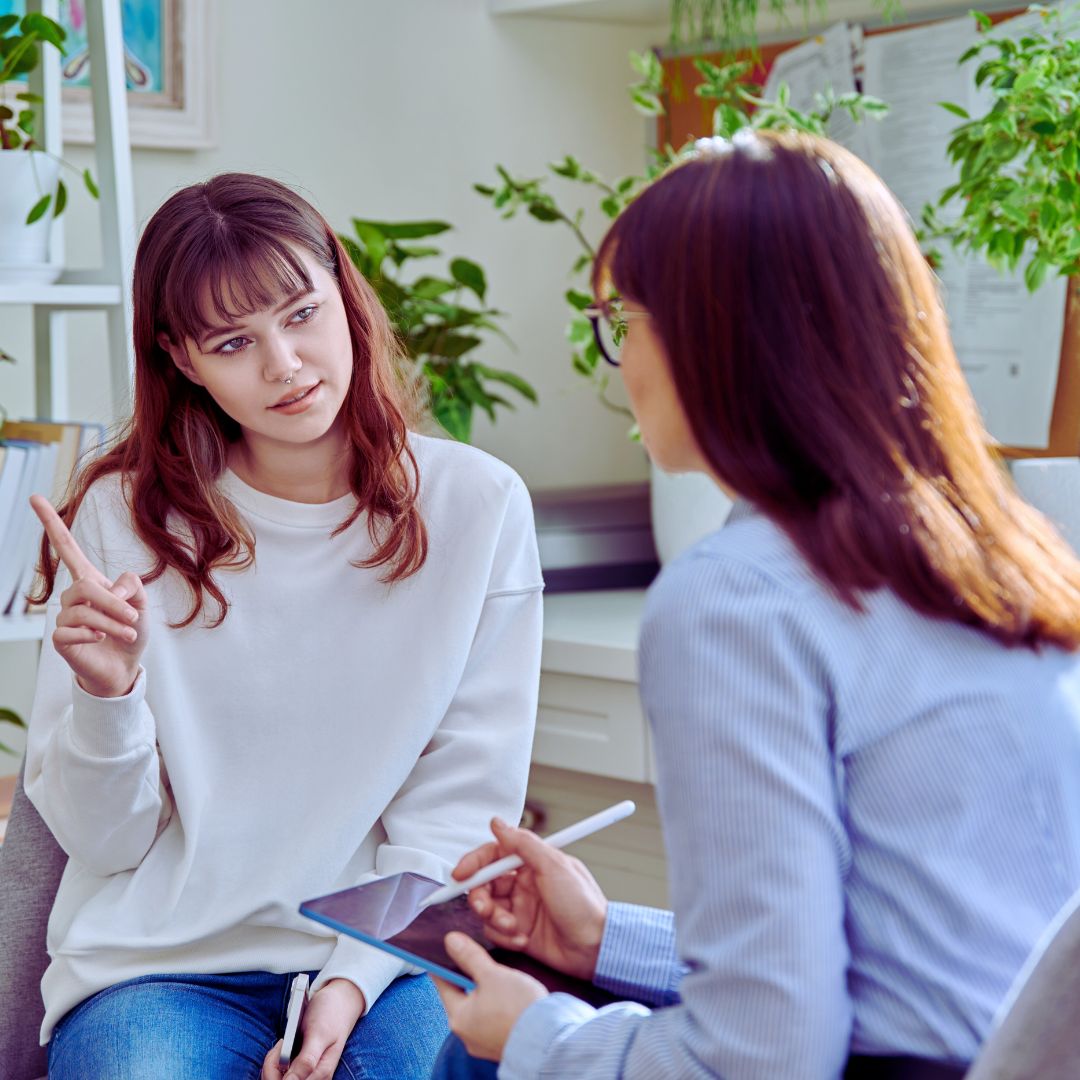
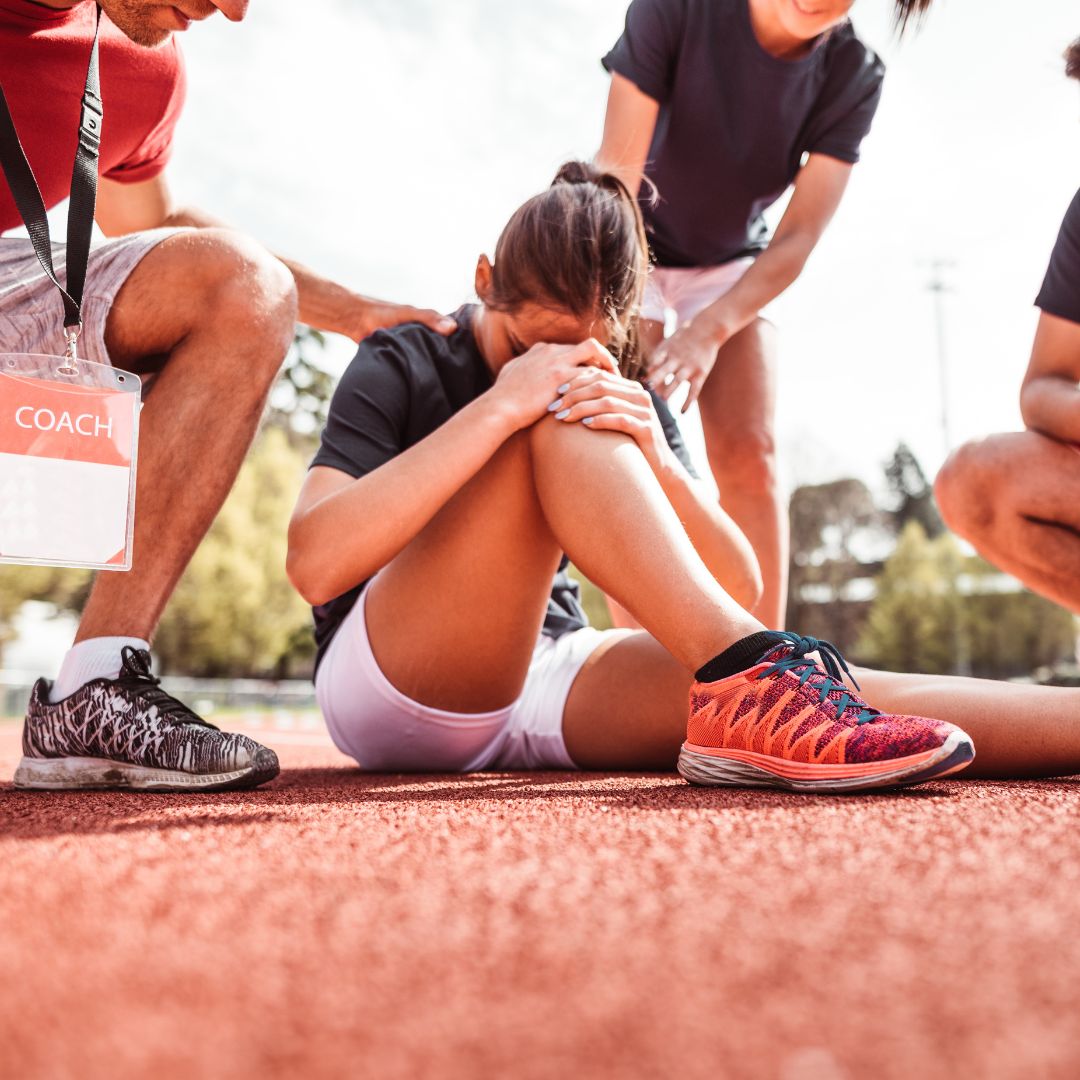
Sports Psychologist in Reston, VA
You want to work on your mental game, but how do you train your brain?
At MindBalanceSPORT, We Train The Other Half Of The Athlete.
You want to work on your mental game, but how do you train your brain?
Mental training does not get much media attention, but at MindBalanceSPORT we know it is a game changer. The mental skills you will learn at MindBalanceSPORT are generalizable in the classroom, in sport and in life!
We know that mental skills can be successfully taught, even at an early age.

Our Services
Meet the Team





testimonials
Athlete Stories: Real Comebacks, Real Results

Emma, a high school basketball player, tore her ACL in the middle of her junior season. After surgery, she struggled with self-doubt and fear every time she stepped back on the court. Through sport psychology training, she learned visualization techniques and confidence-building exercises that helped her regain trust in her knee. When she returned for her senior season, she didn’t just play—she led her team to the playoffs.

Carlos, a soccer player, suffered a stress fracture in his foot and had to miss half of his season. Sitting out was mentally tougher than the pain itself. We worked on mental engagement strategies to keep him sharp—studying game film, setting small rehab goals, and using mental imagery to stay ready. When he was finally cleared, his confidence never wavered.

Jordan, a track athlete, strained her hamstring before a major competition. She feared losing speed and falling behind competitors. Instead of focusing on what she couldn’t do, we redirected her energy toward mental preparation, using self-talk and goal setting to keep her confidence strong. When she returned, she set a new personal record.
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. It was a great help to my 14-year-old competitive volleyball player daughter. Raven was great to understand and connect with her from start to end. We will continue with our sessions as needed.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Great results! I’ve loved working with Paula. Our sessions have greatly improved both the physical and mental aspects of my tennis game. I’m playing better and having more fun! Highly recommend!Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Our family had a wonderful experience with Paula Castro. We needed some additional confidence in a particular area/sport and Paula helped get us there. We know who to turn to if we need help again. She’s been a Blessing. Thank you, Paula!Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I highly recommend MindBalanceSPORT. Our son works with John Howard. John is very caring, positive, and effective at working with teenagers. John is an adept listener and created an individualized plan tailored to our son’s personality. After just a few sessions with John, we noticed a significant improvement in our son’s motivation and mental approach to sports and life in general. Our son looks forward to meeting with John and tells us that he benefits immensely from their connection.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Paula Castro is an outstanding professional on the field. She has helped my daughter improve her confidence, preparation, and thanks to these session she feels more prepared and motivated. Paula takes the time also to share (what she can) and align with us as parents to be on the same page. Strongly recommended!Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. MineBalanceSPORT has quickly become the area's expert in sports psychology. Their reputation is well deserved given their incredibly thoughtful, scientifically based approaches to treating performance-related conditions, and I have only heard glowing, positive feedback from those who have engaged in their program. I will also add that Drs. Jones and Chirby presented to us (our group comprises of 15+ doctors and masters level clinicans) about their program and impressed us all with their level of expertise and passion for this field. I give them my highest recommendation.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr. Jones was beyond helpful to me throughout our time together. If you are an athlete and you need advice or assistance this is the place to come to. She completely changed my outlook and mindset in a time when I needed her most. I look forward to staying in touch with her and am forever thankful for her expertise.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Paula has been a huge help with my daughter Morgan coming off her injury. It’s been 18 months since she’s played basketball and she’s thriving because I know Paula is guiding her the right direction. As a mother, I’m extremely gratefulTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. If you are looking for Amazing Psychologists who can help support you in your sports performance, you need to call MindBalanceSPORT! Dr. Chirby and her colleagues are a wealth of knowledge, they have so many helpful techniques for mind balance, and they have so much compassion for the communities that they serve! Highly recommend!!!
Recovery
While Everyone Has A Physical Ceiling, There Is No Mental Ceiling.
Enhancing Performance and Mental Well-Being Through Sports Counselling in Reston, VA
Enhancing Performance and Mental Well-Being Through Sports Counselling in Reston, VA
Self-compassion has emerged as a crucial psychological tool for athletes striving to improve performance while maintaining their mental well-being. In a highly competitive environment, self-compassion offers a pathway to balancing the demands of sports with healthy emotional management. Rather than harshly critiquing oneself for mistakes or failures, self-compassion encourages kindness, understanding, and constructive evaluation.
What is Self-Compassion?
Self-compassion involves three key elements:
1. Self-kindness: Treating oneself with care rather than harsh criticism in challenging moments.
2. Mindfulness: Acknowledging difficult emotions without over-identifying with them or suppressing them.
3. Common Humanity: Recognizing that struggles and setbacks are part of the shared human experience rather than isolating events.
Incorporating these principles can have profound effects on both athletic performance and mental health.
Why Athletes Struggle Without Self-Compassion
The high-pressure nature of sports often fosters self-critical behavior among athletes. This tendency can lead to:
– Burnout: Unrealistic expectations and harsh self-evaluation may lead to physical and emotional exhaustion.
– Increased Anxiety: Worrying about mistakes or outcomes can negatively impact focus during competition.
– Erosion of Confidence: Persistent self-doubt undermines an athlete’s belief in their abilities, affecting performance over time.
Benefits of Self-Compassion for Athletes
| Benefits | Description |
| Enhanced Resilience | Athletes bounce back more effectively from failures or injuries when they are less self-critical. |
| Improved Focus | Letting go of negative thoughts allows athletes to remain present during games or competitions. |
| Reduced Stress Levels | Accepting imperfection helps alleviate the pressure associated with constant success. |
| Greater Motivation | Encouragement fosters effort toward improvement without fear of failure. |
Research suggests that athletes who practice self-compassion are better equipped to face challenges with confidence and clarity.
Tips for Cultivating Self-Compassion in Sports
- Practice Positive Self-Talk: Replace negative thoughts like “I’m terrible” with affirmations such as “I’m learning and improving.”
- Learn from Mistakes: View errors as opportunities for growth rather than reasons for punishment.
- Set Realistic Goals: Avoid setting unattainable objectives; focus on personal progress instead.
- Seek Support When Needed: Working with a sports psychologist or counselor can provide strategies tailored to individual needs.
- Engage in Mindfulness Practices: Techniques like meditation and deep breathing foster a nonjudgmental awareness of emotions.
By fostering self-compassion, athletes become not only better performers but also more resilient individuals capable of thriving both on and off the field.
Exploring Performance Psychology in Reston, VA: The Impact of Self-Compassion on Athletic Success and Mental Resilience
In the competitive world of sports, athletes often face immense pressure to perform at their peak, overcome challenges, and meet both external and internal expectations. While physical skill and training are critical elements of success, mental resilience plays an equally essential role in determining performance outcomes. At the heart of mental strength lies self-compassion—a concept that is increasingly recognized as a cornerstone for enhancing athletic performance and maintaining emotional well-being.
What Is Self-Compassion?
- Self-kindness over self-criticism: Acknowledging imperfections without harsh judgment.
- Common humanity over isolation: Recognizing that struggles are a shared human experience rather than something faced alone.
- Mindfulness over rumination: Maintaining a balanced perspective on one’s thoughts and feelings without over-identifying with them.
For athletes who tend to be their harshest critics, adopting self-compassion can create a healthier relationship with themselves and their sport.
How Self-Compassion Impacts Athletic Performance
- Athletes who practice self-compassion are better equipped to manage stress, anxiety, and frustration during high-stakes competitions or when recovering from losses. This emotional balance enables them to focus more effectively on their goals.
- Contrary to the belief that being self-critical drives progress, research suggests that self-compassion sustains motivation by encouraging persistence after setbacks rather than feelings of inadequacy or defeat.
- Dwelling on mistakes can distract athletes from staying present during performance. Self-compassion helps them accept errors without fixating on them, allowing for greater concentration moving forward.
- Sports often involve unpredictable situations. A self-compassionate mindset reduces the fear of failure by promoting adaptability and confidence when facing adversity.
Building Mental Resilience Through Self-Compassion
| Strategy | Description |
| Practicing Positive Self-Talk | Replacing negative inner dialogue with affirming language to build confidence |
| Normalizing Failure | Encouraging athletes to view mistakes as opportunities for learning |
| Mindfulness Techniques | Teaching grounding exercises like meditation or breathing practices |
| Journaling | Promoting reflection on strengths, growth areas, and accomplishments |
By integrating these techniques into training routines or recovery periods post-competition, athletes can develop habits that improve their psychological well-being alongside their physical prowess.
Long-Term Benefits Beyond Athletics
The advantages of self-compassion extend beyond sports into broader life experiences. Athletes who embrace this mindset are likely to face challenges outside the athletic arena—such as career transitions or personal relationships—with increased resilience and emotional stability.
Ultimately, fostering self-compassion not only benefits athletic performance but also promotes overall mental health—a critical element for sustained success in both professional endeavors and personal growth journeys.
The Importance of Self-Compassion in Sport Performance Training in Reston, VA
Self-compassion, a concept rooted in positive psychology, is increasingly recognized as a key tool for athletes to enhance their performance and build mental resilience. Despite the highly competitive nature of sports, where athletes often push themselves relentlessly to achieve peak performance, self-compassion can act as a buffer against the negative consequences of self-criticism and burnout.
What Is Self-Compassion?
- Self-Kindness – Being supportive toward oneself rather than harshly critical.
- Common Humanity – Recognizing that struggles are part of the shared human experience.
- Mindfulness – Maintaining a balanced perspective about one’s emotions, neither suppressing nor exaggerating them.
Rather than viewing self-compassion as weakness or indulgence, research shows that it enhances motivation and fosters emotional resilience.
Benefits for Athletic Performance
- Reduced Fear of Failure: Athletes who practice self-compassion are less likely to dwell on mistakes or failures. This allows them to recover quickly from setbacks during training or competition.
- Enhanced Focus on Growth: Instead of being paralyzed by perfectionism, self-compassionate athletes tend to focus on learning from challenges and improving their skills.
- Improved Motivation: Studies indicate that being kind to oneself leads to sustainable motivation driven by values rather than external pressures or fear.
| Benefit | How It Helps Athletes |
| Reduced fear of failure | Encourages quicker recovery from setbacks |
| Enhanced focus on growth | Promotes learning from mistakes instead of dwelling on them |
| Improved motivation | Drives intrinsic, long-term efforts |
Building Mental Resilience Through Self-Compassion
- Stress Management: By reframing challenges with self-kindness, athletes can approach high-pressure situations with calmness and clarity.
- Emotional Regulation: Mindful acknowledgment of emotions—without judgment—prevents emotional outbursts or suppression.
- Longevity in Sports: A balanced approach reduces the risk of athlete burnout caused by chronic stress and perfectionism.
Practical Strategies for Cultivating Self-Compassion
- Develop Positive Self-Talk: Replace harsh critiques like “I’ll never succeed” with affirmations such as “I’m working hard and growing every day.”
- Practice Mindfulness: Use meditation or breathing exercises to stay grounded in the present moment without judgment.
- Reframe Setbacks: View failures as opportunities for growth rather than personal inadequacies.
- Keep a Journal: Reflect on daily experiences while acknowledging both successes and areas for improvement through a lens of kindness.
The Takeaway
By embracing self-compassion as part of their mental training toolkit, athletes can not only enhance their performance but also safeguard their mental health throughout their career journey. This psychological skill empowers them to face adversity with grace while cultivating sustainable motivation for success over time.
How a Sports Mental Coach in Reston, VA Impacts Athlete Success and Personal Growth
Sports psychology plays a foundational role in shaping the success and holistic growth of athletes. It is not solely about improving performance but also about fostering mental resilience, promoting well-being, and helping athletes navigate the unique challenges they encounter. Below, we explore the key implications of sports psychology on both athletic success and personal development.
Enhancing Athletic Performance
- Goal-Setting Techniques:
Athletes are taught to set SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) that improve focus and accountability. - Mental Imagery Training:
Visualization techniques allow athletes to mentally rehearse their performance, building confidence and reducing anxiety before events. - Stress Management:
Strategies such as mindfulness, deep-breathing exercises, or progressive muscle relaxation enable athletes to stay calm under pressure. - Attention Control:
Concentration drills help improve focus during critical moments in games or competitions.
| Technique | Purpose | Example |
| Goal-setting | Clarify objectives and improve focus | Setting short-term milestones |
| Visualization/Imagery | Mentally rehearse scenarios | Picturing successful free throws |
| Relaxation training | Reduce stress and physical tension | Deep-breathing exercises |
| Positive self-talk | Build confidence and motivation | Replacing negative thoughts |
Building Mental Resilience
- Cognitive Restructuring: Teaching athletes how to reframe negative thoughts into constructive ones.
- Resilience Training Programs: Strengthening coping mechanisms for setbacks or injuries.
- Developing Self-Awareness: Encouraging reflection on emotional triggers that affect performance.
These tools equip athletes with the emotional fortitude needed to handle high-stress situations effectively.
Promoting Personal Growth Beyond Performance
- Improved Self-Esteem: Regular engagement with sports psychologists helps athletes develop a healthy sense of self-worth that isn’t tied exclusively to wins or losses.
- Work-Life Balance: Athletes often deal with demanding schedules; psychologists guide them in maintaining balance between their sport, social life, and personal aspirations.
- Ethical Decision-Making: By promoting accountability and reflective practices, sports psychology contributes to ethical behavior both on and off the field.
- Coping with Transitions: Athletes retiring from competitive sports often struggle with identity loss. Sports psychologists assist in this transition by helping individuals redefine their purpose beyond athletics.
The Broader Impact
- It fosters a team culture built on mutual support through shared psychological strategies.
- Coaches benefit significantly by learning athlete-centered communication styles promoted by sports psychologists.
- Organizations see improved well-being among their players alongside better overall results in competition.
By addressing both athletic success and personal development holistically, sports psychology proves itself an indispensable element for any athlete’s journey toward peak performance while nurturing long-term well-being.
How Sports Psychiatry in Reston, VA Helps Athletes Tackle Body Image Issues and Eating Concerns
Body image issues and disordered eating can significantly impact an athlete’s performance, mental health, and overall well-being. Sports psychologists play a vital role in addressing these challenges by providing tailored strategies, promoting healthy mindsets, and fostering resilience. Their work involves understanding the unique pressures athletes face while helping them develop sustainable habits to maintain both physical and mental health.
Understanding the Root Causes of Body Image Issues
- Performance Expectations: Pressure to meet specific body standards for improved athletic performance (e.g., low body fat for runners or lean muscle mass for gymnasts).
- Cultural Norms in Sports: Certain sports inherently emphasize physical appearance, shaping expectations around “ideal” bodies.
- Social Comparison: Comparing themselves to teammates, competitors, or media portrayals of athletes.
- Internal Factors: Low self-esteem or perfectionistic tendencies that exacerbate negative feelings about appearance.
Understanding these triggers allows sports psychologists to design interventions that address both environmental and personal influences.
Strategies Employed by Sports Psychologists
- Helps athletes identify distorted thought patterns related to body image and challenge those misconceptions.
- Encourages healthier perspectives on food, exercise, and self-worth.
- Promotes awareness of thoughts without judgment.
- Reduces emotional reactivity tied to external pressures about appearance or weight.
- Educates athletes about the vital role balanced nutrition plays in optimizing performance.
- Reshapes their focus from aesthetic goals to functional goals supporting their sport.
- Encourages appreciation for what their bodies can achieve rather than how they look.
- Uses affirmations or gratitude practices centered around physical abilities.
Collaboration with Other Professionals
| Professional | Role |
| Dietitians/Nutritionists | Provide personalized dietary plans promoting health & performance |
| Coaches | Foster a supportive training environment free from undue pressure on aesthetics |
| Medical Practitioners | Address physical health concerns like nutrient deficiencies or eating disorders |
This multidisciplinary approach ensures that both psychological and physiological aspects are addressed effectively.
Preventative Measures: Promoting a Healthy Athletic Culture
- Education & Awareness Campaigns: Programs highlighting the risks of disordered eating and unrealistic body ideals.
- Positive Coaching Practices: Training coaches to prioritize mental well-being over superficial metrics like weight or size.
- Role Modeling Healthy Behaviors: Encouraging teams to value diversity in body types rather than adhering strictly to stereotypes.
By creating environments where athletes feel supported both mentally and physically, sports psychologists empower individuals while minimizing the risk of long-term harm caused by body image issues or disordered eating habits.
Addressing these challenges is essential not only for maintaining peak performance but also for ensuring long-term emotional resilience among athletes across all levels of competition.
How Sports Psychologists in Reston, VA Provide Crucial Mental Health Support for Athletes
Mental health is a critical component of overall well-being, and for athletes, it often plays a decisive role in their performance, resilience, and longevity in their respective sports. Despite the physical focus within athletics, mental health challenges such as anxiety, depression, stress, or burnout are increasingly recognized as significant factors that require attention. Sports psychologists specialize in providing mental health support tailored to the unique demands and pressures athletes face.
Finding the Right Sports Psychologist Near Me: Why Mental Health Support Matters for Athletes
- Stress Management: Balancing training schedules, competition pressures, and personal responsibilities can create overwhelming stress.
- Performance Anxiety: Fear of failure or underperforming often leads to anxiety before or during competitions.
- Burnout Prevention: Overtraining or lack of work-life balance can cause physical exhaustion coupled with emotional detachment.
- Identity Issues: Athletes may struggle with self-worth outside their sport or face challenges transitioning after retirement.
- Trauma Recovery: Injuries or high-profile setbacks can take an emotional toll on athletes.
How Sports Psychologists Provide Support
1. Developing Coping Strategies
Sports psychologists teach athletes techniques such as: – Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) to cultivate present-moment awareness. – Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to reframe negative thought patterns around performance. – Breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation for managing acute anxiety.
2. Enhancing Emotional Regulation
Athletes learn to acknowledge and manage emotions effectively rather than suppress them: | Emotion | Tool | Example | |———|——|———| | Anger | Controlled breathing | Taking deep breaths after errors during competition | | Fear | Visualization | Imagining overcoming obstacles before events | | Frustration | Journaling | Reflecting on setbacks constructively |
3. Building Resilience
Resilience-focused interventions empower athletes to adapt positively to challenges: – Goal-setting strategies enhance focus by setting realistic short-term objectives alongside long-term aspirations. – Self-compassion exercises encourage athletes to treat themselves kindly during failures rather than engaging in self-criticism.
Breaking the Stigma Around Mental Health in Sports
Despite progress, stigma around seeking mental health support persists among many athletes who fear being perceived as “weak” for asking for help. However: – High-profile advocates like Simone Biles and Michael Phelps have openly discussed their struggles with mental health, helping normalize these conversations. – Teams and organizations are increasingly embedding psychological services into athletic programs.
Promoting awareness about the benefits of mental health support not only helps individuals thrive but also fosters healthier team dynamics.
By prioritizing both physical and psychological fitness equally, sports psychologists enable athletes at all levels—from recreational participants to elite professionals—to unlock their full potential while safeguarding their overall well-being.